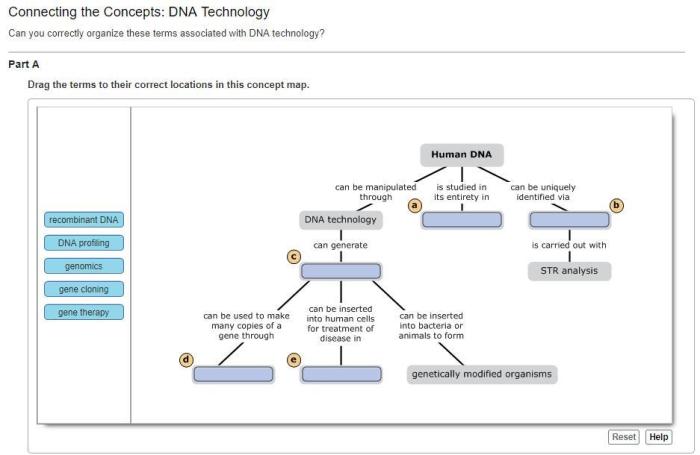
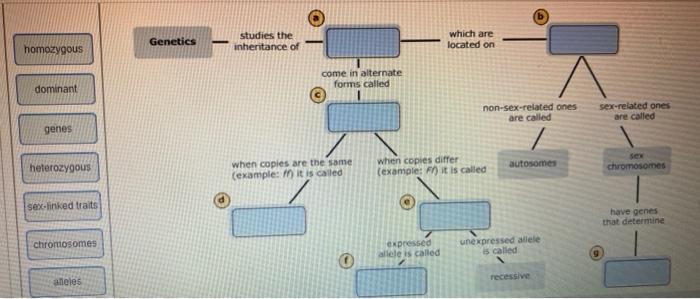
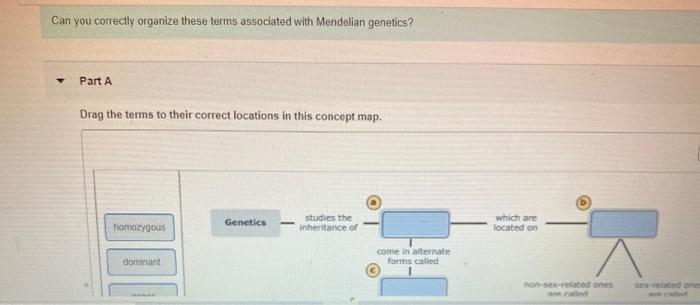
Can you correctly organize these terms associated with clonal selection? This question may seem daunting at first, but with a clear understanding of the key concepts involved, it becomes much easier. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of clonal selection theory, including its key terms, stages, and applications.
By the end, you will have a solid foundation in this fundamental aspect of adaptive immunity.
Clonal selection theory is a central concept in immunology that explains how the immune system recognizes and responds to foreign invaders. It proposes that each T cell is specific for a particular antigen and that upon encountering its cognate antigen, the T cell will proliferate and differentiate into effector and memory cells.
This process, known as clonal selection, is essential for the development of an effective immune response.
Clonal Selection Theory: Can You Correctly Organize These Terms Associated With Clonal Selection
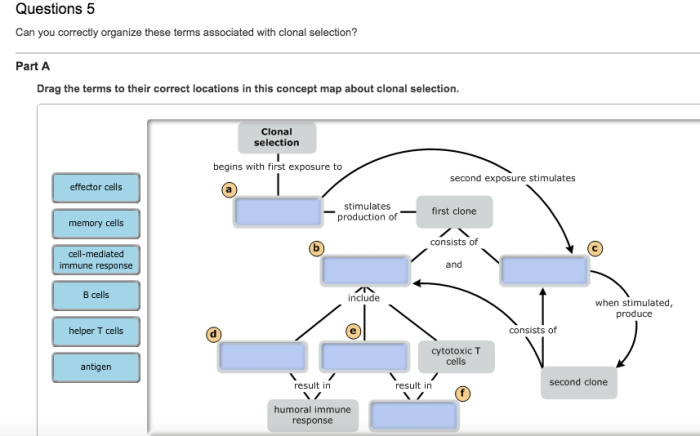
Clonal selection theory is a fundamental concept in immunology that explains how the adaptive immune system recognizes and responds to specific antigens. It provides a framework for understanding the generation of diverse immune cells and the development of immunological memory.
Key Terms Associated with Clonal Selection
- Clonal selection:The process by which a specific antigen-specific T cell is selected and expanded to generate a population of effector and memory T cells.
- Antigen-presenting cells (APCs):Cells that display antigens on their surface, allowing T cells to recognize and respond to them.
- T cell receptors (TCRs):Molecules on the surface of T cells that recognize and bind to specific antigens presented by APCs.
- Clonal expansion:The proliferation of antigen-specific T cells following antigen recognition and activation.
Stages of Clonal Selection, Can you correctly organize these terms associated with clonal selection
- Initiation:Antigen recognition by TCRs on T cells and subsequent T cell activation.
- Proliferation:Expansion of antigen-specific T cells through cell division.
- Differentiation:Development of effector T cells (responsible for eliminating pathogens) and memory T cells (provide long-term immunity).
- Regulation:Control of clonal expansion and T cell responses to prevent excessive or inappropriate immune responses.
Applications of Clonal Selection Theory
- Vaccine development:Understanding clonal selection allows for the design of vaccines that stimulate the immune system to generate protective antibodies and T cells.
- Autoimmune diseases:Clonal selection theory helps explain the mechanisms underlying autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues.
- Cancer immunotherapy:Clonal selection provides a basis for developing immunotherapies that harness the immune system to target and eliminate cancer cells.
- Regenerative medicine:Clonal selection principles could be applied to generate immune cells for tissue repair and regeneration.
Query Resolution
What is clonal selection theory?
Clonal selection theory is a theory that explains how the immune system recognizes and responds to foreign invaders. It proposes that each T cell is specific for a particular antigen and that upon encountering its cognate antigen, the T cell will proliferate and differentiate into effector and memory cells.
What are the key terms associated with clonal selection?
The key terms associated with clonal selection include:
- Antigen
- T cell
- B cell
- Antibody
- Clonal expansion
- Effector T cell
- Memory T cell
What are the stages of clonal selection?
The stages of clonal selection include:
- Antigen recognition
- T cell activation
- Clonal expansion
- Differentiation
- Effector function
- Memory formation
What are the applications of clonal selection theory?
Clonal selection theory has a wide range of applications, including:
- Vaccines
- Autoimmune diseases
- Cancer immunotherapy
- Regenerative medicine