Draw the major organic product of the reaction conditions shown. This comprehensive guide unveils the intricate world of organic reactions, empowering you to predict and interpret the outcomes of these fundamental chemical transformations. Delve into the factors that govern the formation of major organic products, unraveling the secrets of reaction conditions and their profound impact on the molecular landscape.
As we embark on this journey, we will explore the diverse types of organic reactions, deciphering the mechanisms that drive their outcomes. We will equip you with a step-by-step approach to drawing major organic products, empowering you to visualize and understand the intricate dance of atoms and molecules.
Introduction to Organic Reactions
Organic reactions are chemical transformations involving compounds containing carbon. They play a crucial role in chemistry, enabling the synthesis of complex molecules, pharmaceuticals, materials, and more.
Organic reactions can be classified into various types based on the nature of the change, such as addition, elimination, substitution, and rearrangement reactions.
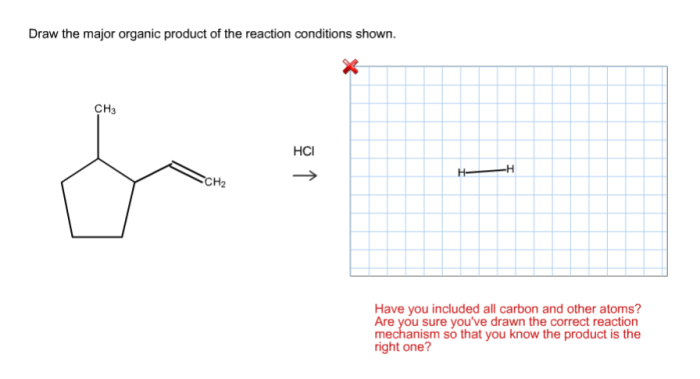
Major Organic Product: Draw The Major Organic Product Of The Reaction Conditions Shown.
The major organic product in an organic reaction is the most abundant product formed under specific reaction conditions.
Factors influencing the formation of the major organic product include the starting materials, reaction conditions, and the reaction mechanism.
Reaction Conditions
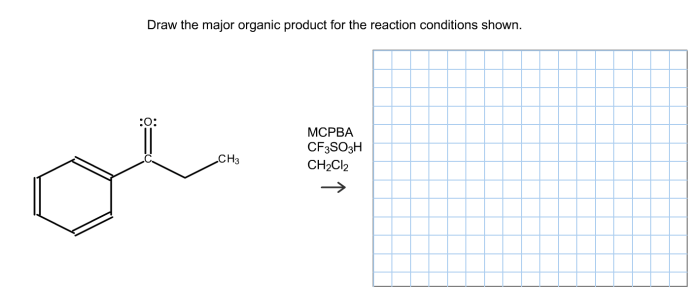
Reaction conditions significantly impact the outcome of an organic reaction.
Temperature:Higher temperatures generally increase reaction rates and favor products with lower activation energies.
Pressure:Increased pressure can favor reactions involving gases or reactions that result in a decrease in volume.
Solvent:Solvents can influence reaction rates, solubility, and the stability of intermediates.
Catalysts:Catalysts accelerate reactions by providing an alternative pathway with a lower activation energy.
Drawing the Major Organic Product
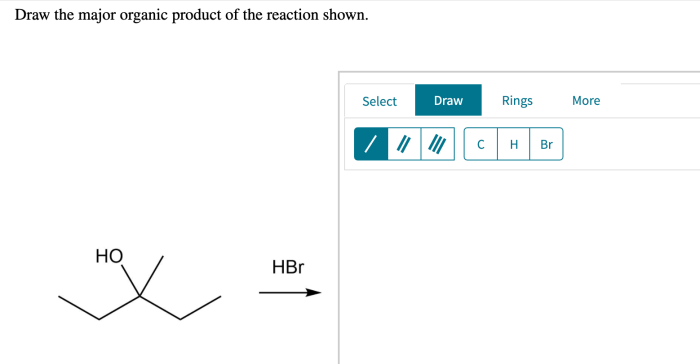
To draw the major organic product:
- Identify the starting materials and reaction conditions.
- Determine the possible reaction mechanisms.
- Use chemical structures and arrows to represent the steps of the mechanism.
- Identify the intermediate and transition state structures.
- Draw the product(s) formed from the lowest energy pathway.
Examples and Applications
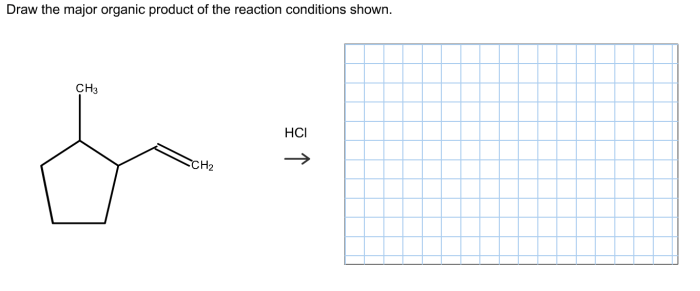
Example:The reaction of an alcohol with a carboxylic acid in the presence of an acid catalyst yields an ester.
Application:Organic reactions are used in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and environmental chemistry.
Quick FAQs
What is the significance of drawing the major organic product?
Drawing the major organic product provides valuable insights into the outcome of a reaction, enabling the prediction and interpretation of product formation. It serves as a roadmap for understanding the reaction pathway and the factors that influence the product distribution.
How do reaction conditions affect the formation of the major organic product?
Reaction conditions, such as temperature, pressure, solvent, and catalysts, play a crucial role in determining the major organic product. These conditions can influence the reaction pathway, alter the stability of intermediates, and affect the selectivity of the reaction.