Resonant frequency capacitive coupling and dielectric breakdown are examples of – Resonant frequency, capacitive coupling, and dielectric breakdown are fundamental concepts in electronics that play critical roles in the design and performance of electronic devices. Understanding these concepts is essential for engineers and students alike.
This article explores the nature, applications, and design considerations of resonant frequency, capacitive coupling, and dielectric breakdown, providing a comprehensive overview of these important topics.
Resonant Frequency

Resonant frequency is a crucial concept in electronic circuits. It refers to the specific frequency at which a circuit or system exhibits maximum amplitude of oscillation or resonance. When an AC voltage is applied to a circuit, the current and voltage oscillate at a particular frequency.
If the frequency of the applied voltage matches the resonant frequency of the circuit, the amplitude of the oscillations reaches a peak.
Resonant frequency is determined by the circuit’s inductance (L) and capacitance (C), and is given by the formula: f = 1 / (2π√LC).
Resonant frequency plays a significant role in electronic devices, including filters, oscillators, and antennas. By adjusting the resonant frequency, engineers can optimize the performance and functionality of these devices.
Applications of Resonant Frequency
- Filters: Resonant circuits are used in filters to selectively pass or reject specific frequencies.
- Oscillators: Resonant circuits are used in oscillators to generate stable and precise AC signals.
- Antennas: Resonant antennas are designed to transmit or receive electromagnetic waves at a specific resonant frequency.
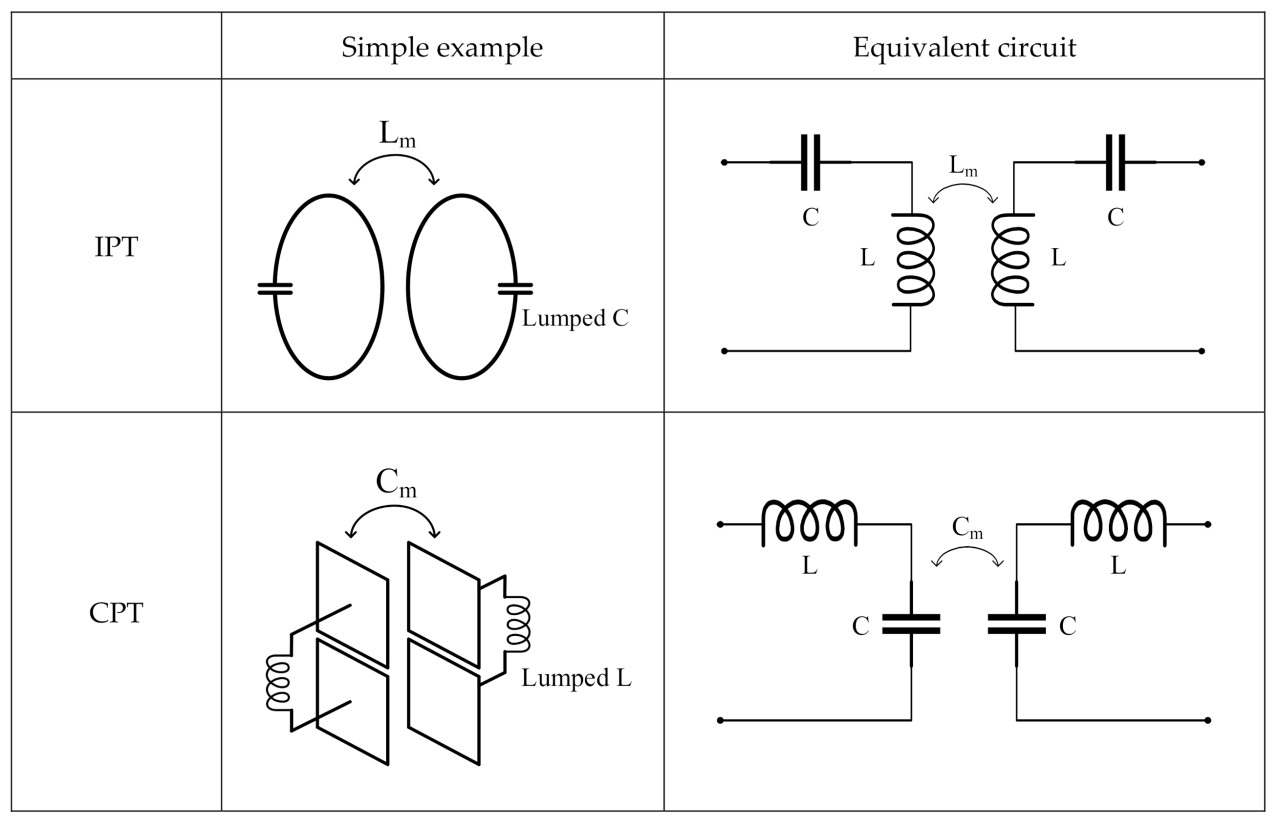
Capacitive Coupling
Capacitive coupling is a mechanism that allows electrical signals to be transferred between two conductors separated by an insulating material called a dielectric. When a voltage is applied to one conductor, an electric field is created, which induces an opposite charge on the other conductor.
This charge separation creates a capacitance between the conductors.
The strength of capacitive coupling depends on several factors, including the area of the conductors, the distance between them, and the permittivity of the dielectric material.
Capacitive coupling is commonly used in electronic circuits for various purposes, such as signal filtering, impedance matching, and voltage isolation.
Applications of Capacitive Coupling
- Signal filtering: Capacitors are used in filters to block or pass specific frequency components of a signal.
- Impedance matching: Capacitive coupling is used to match the impedance of a source to a load, ensuring efficient power transfer.
- Voltage isolation: Capacitors are used for voltage isolation in circuits, preventing direct current from flowing between two circuits while allowing AC signals to pass.
Dielectric Breakdown
Dielectric breakdown is a phenomenon that occurs when the electric field strength across a dielectric material exceeds its dielectric strength. When this happens, the dielectric material loses its insulating properties and becomes conductive, allowing current to flow through it.
The dielectric strength of a material depends on its chemical composition, physical structure, and temperature. Factors such as impurities, defects, and high temperatures can reduce the dielectric strength of a material.
Dielectric breakdown can lead to short circuits, equipment failure, and safety hazards. Therefore, it is crucial to select appropriate dielectric materials and design circuits to avoid dielectric breakdown.
Applications of Dielectric Breakdown, Resonant frequency capacitive coupling and dielectric breakdown are examples of
- Lightning arrestors: Dielectric breakdown is utilized in lightning arrestors to protect electrical equipment from lightning strikes.
- Circuit breakers: Dielectric breakdown is used in circuit breakers to interrupt current flow when a fault occurs.
- High-voltage capacitors: Dielectric breakdown limits the maximum voltage that can be applied to capacitors.
Examples and Applications: Resonant Frequency Capacitive Coupling And Dielectric Breakdown Are Examples Of

| Technique | Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resonant Frequency | Filters, oscillators, antennas | – Precise frequency selection
|
– Sensitive to component variations
|
| Capacitive Coupling | Signal filtering, impedance matching, voltage isolation | – Signal isolation
|
– Capacitance variation with temperature
|
| Dielectric Breakdown | Lightning arrestors, circuit breakers, high-voltage capacitors | – Voltage protection
|
– Material degradation
|
Design Considerations
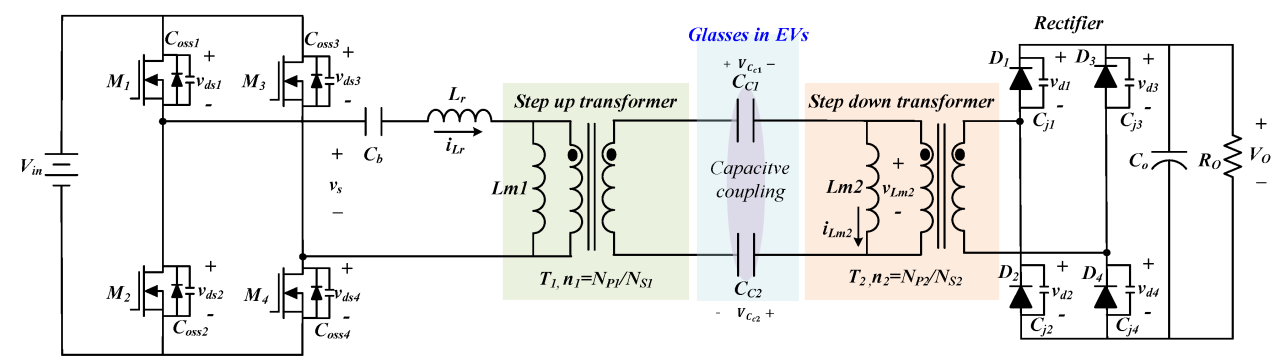
When using resonant frequency, capacitive coupling, and dielectric breakdown in electronic circuits, several key design considerations must be taken into account:
- Resonant frequency:The resonant frequency of a circuit must be carefully selected to meet the desired performance requirements. Factors such as component tolerances, stability, and power handling must be considered.
- Capacitive coupling:The capacitance value and physical arrangement of the conductors must be optimized to achieve the desired coupling strength and minimize parasitic effects.
- Dielectric breakdown:The dielectric material must be carefully selected and the electric field strength must be kept below the dielectric strength to avoid breakdown.
By considering these design considerations, engineers can optimize the performance and reliability of electronic circuits that utilize resonant frequency, capacitive coupling, and dielectric breakdown.
Essential Questionnaire
What is resonant frequency?
Resonant frequency is the frequency at which an electrical circuit exhibits maximum impedance or minimum impedance.
What is capacitive coupling?
Capacitive coupling is the transfer of energy between two conductors through an electric field.
What is dielectric breakdown?
Dielectric breakdown is the failure of an insulating material under the application of an electric field.